Cistrome Cancer
Cistrome Cancer is a comprehensive resource for predicted transcription factor (TF) targets and enhancer profiles in cancers. The prediction was from integrative analysis of TCGA expression profiles and public ChIP-seq profiles.
Cancer Enhancer Prediction
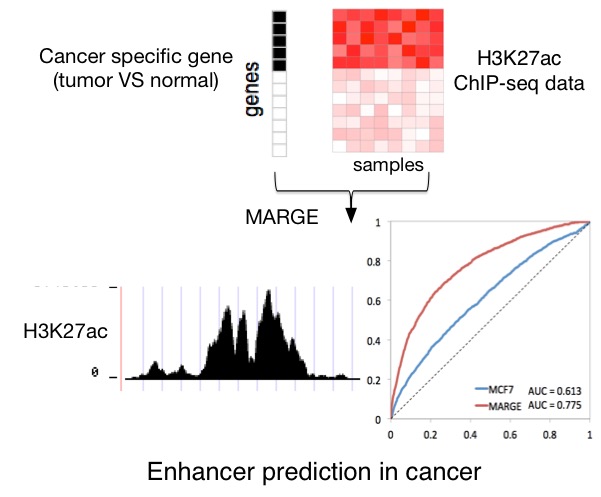
Cancer Enhancer Prediction used publicly available H3K27ac ChIP-seq profiles and chromatin accessibility DNase-seq profiles to predict cis-regulatory profiles that mark functional enhancers regulating specific active genes in each cancer type. We used Model-based Analysis of Regulation of Gene Expression (MARGE) to do enhancer prediction. MARGE-predicted enhancer profiles are available for download or direct visualization using WashU genome browser or UCSC genome browser. Cancer-specific genes and MARGE retrieved integrative RP score for each gene are also available for download, where genes with high-ranked RP scores are “super-enhancer” target cancer type specific genes.
TCGA cancer type clusters
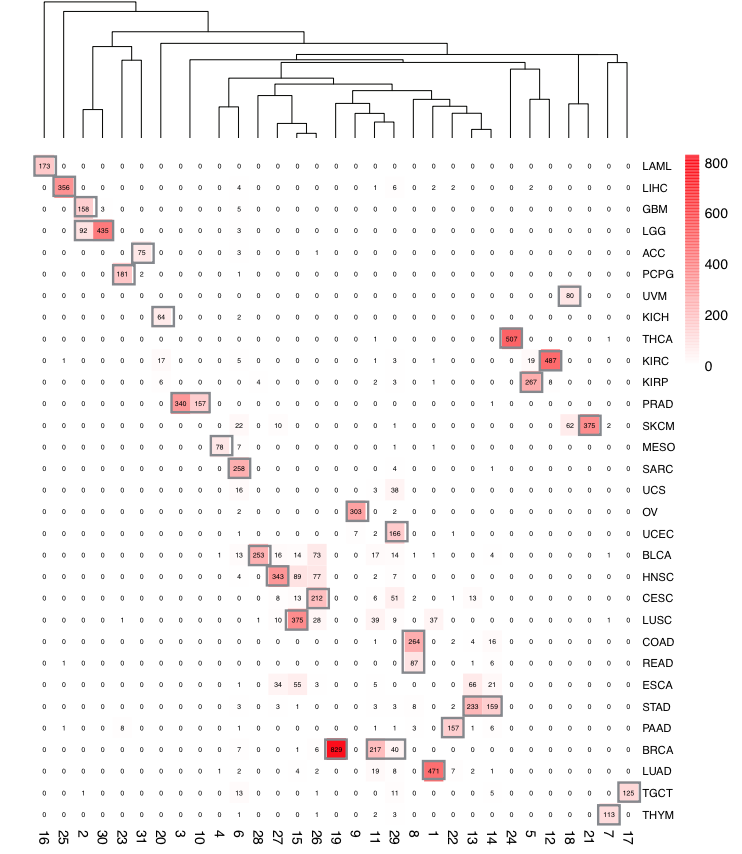
In order to obtain robust and consistent cancer types, over 13 thousand TCGA expression profiles (RNA-seq) from all cancer samples were re-clustered using K-means clustering and 29 cancer clusters were retained. As a result, some unambiguous cancer subtypes were separated as different clusters (e.g. BRCA_1 for basal and BRCA_2 for luminal), while some similar cancer types are merged as one cluster and renamed with the representative cancer type with an asterisk (e.g. COAD and READ as COAD_READ*). Cancer type abbreviations were following the TCGA cancer abbreviations (https://tcga-data.nci.nih.gov/tcga/). For simplicity, we refer to the redefined cancer clusters as “cancer types” thereafter.
Workflow
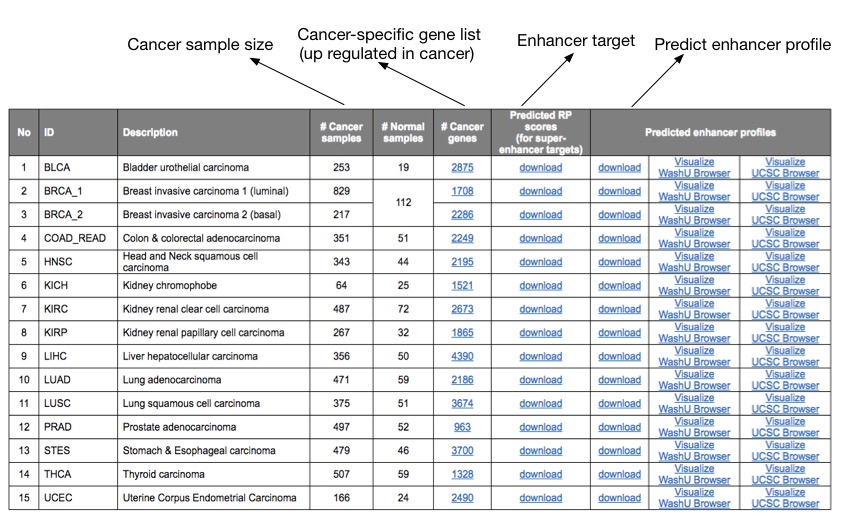
For each cancer type, cancer-specific genes, defined as up-regulated genes in the cancer samples compared with normal samples, were first identified by analyzing the TCGA transcriptomic RNA-seq data using VOOM-LIMMA with a p-value cutoff of 0.01 and fold-change cutoff of 2. Eliminating the cancer types with less than 10 available normal samples for robust differential expression analysis, we obtained cancer-specific gene sets for 15 cancer types. The MARGE-express module was used to generate functional enhancer profiles for each cancer type, integrating information from over 1,200 H3K27ac ChIP-seq datasets collected in the Cistrome DB database. MARGE defines a regulatory potential (RP) score for each gene by summarizing nearby H3K27ac ChIP-seq signals and uses logistic regression to retrieve relevant public H3K27ac profiles that accurately model gene sets of interest. MARGE adopts a semi-supervised learning approach to identify the enhancers regulating these genes. In order to get optimized results, MARGE was run 5 times for each cancer type and the prediction with the highest ROC-AUC score was selected as the output result.
MARGE-predicted enhancer profiles are available for download or direct visualization using WashU genome browser or UCSC genome browser. Cancer-specific genes and MARGE retrieved integrative RP score for each gene are also available for download, where genes with high-ranked RP scores are “super-enhancer” target cancer type specific genes.